
Scoliosis is more than just an abnormal sideways curvature of the spine; it often includes a rotational component that traditional braces or surgical solutions,...
Learn more
Scoliosis is a complex condition that affects not only the spine but also the nervous system, ligaments, and muscles. It is a three-dimensional problem, m...
Learn moreChiropractic care complements other modalities like physical therapy and massage therapy, providing a comprehensive approach to pain management. By addres...
Learn more
At All Well Scoliosis Centre, we understand that pain in areas like the neck, shoulders, elbows, back, knees, and ankles are often interconnected. These p...
Learn more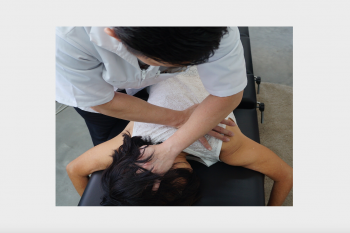
Neck and back pain can arise from various causes, including poor posture ("Text neck"), sedentary lifestyle, prolonged use of electronic devices, whiplash injur...
Learn more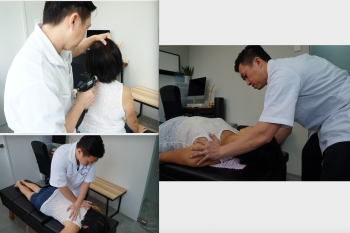
Chiropractic care is a cornerstone of our approach to managing neck, back, shoulder, knee pain and similar. By focusing on spinal alignment, joint functio...
Learn more
Hill Decompression Therapy (Hill DT) is an advanced technique we use to treating slipped discs, bulging discs, and other spinal issues. Misalignments...
Learn more
Maintaining flexiblity and mobility is key to preventing injuries, especially for athletes and active individuals. Overuse, poor posture, and muscle imbal...
Learn more